"Cannot unmount volume because" error unmounting a datastore
Article ID: 321318
Updated On:
Products
VMware vSphere ESXi
Issue/Introduction
Symptoms:
- You cannot unmount a datastore using the vSphere Client.
- You see the error:
Cannot unmount volume Datastore_details because Reason. Correct the problem and retry the operation.
Where reason can be any of these:
- One or more virtual machines are still registered on it
- Swap to host cache is enabled on it
- Storage I/O Control is either enabled or running in statistics collection mode on it
- File system is busy
Environment
VMware vSphere 6.x
VMware vSphere 7.x
VMware vSphere 7.x
VMware vSphere 8.x
Cause
If ESXi host is actively using a datastore, the unmount operation on the datastore fails. The unmount operation of a seemingly inactive datastore can also fail if ESXi host has any open file handles on that datastore.
These are some of the cases where a seemingly inactive datastore can be actively in use:
- If there are virtual machines or templates residing on that datastore, that are still registered in the vCenter Server Inventory.
- If services such as Storage I/O Control (SIOC) is enabled on the datastore.
- If the Swapping to host cache or Host-local swap option is turned on and this datastore is in use to store the swap files of virtual machines.
For more information, see the Using Swap Files section in the vSphere Resource Management Guide . - If ESXi coredump is configured to a file on the datastore instead of a coredump partition.
- If services such as syslog or trace files are configured to be stored on the datastore.
- vCenter cluster services are configured to the datastore.
Resolution
If unmounting a datastore fails because virtual machines or templates from the datastore are still registered, then unregister those virtual machines, templates and retry the unmount operation. For more information, see the Remove Virtual Machines from vCenter Server section in the vSphere Virtual Machine Administration guide.
If unmounting a datastore fails because Storage I/O Control (SIOC) was enabled on the datastore, disable the SIOC service on the datastore and retry the operation. For more information, see Unmounting an inactive datastore fails with the error: Cannot remove datastore 'datastore_name' because Storage I/O Control is enabled on it.
If unmounting a datastore fails because the Host-Local Swap feature was enabled in the datastore, reconfigure the virtual machine swap file properties to use a different datastore or to store the swap files in the virtual machine directories. For more information, see Configure Virtual Machine Swapfile Properties for the Host section in the vSphere Resource Management guide.
If unmounting a datastore fails because the underlying filesystem is busy, then perform these steps.
If unmounting a datastore fails because Storage I/O Control (SIOC) was enabled on the datastore, disable the SIOC service on the datastore and retry the operation. For more information, see Unmounting an inactive datastore fails with the error: Cannot remove datastore 'datastore_name' because Storage I/O Control is enabled on it.
If unmounting a datastore fails because the Host-Local Swap feature was enabled in the datastore, reconfigure the virtual machine swap file properties to use a different datastore or to store the swap files in the virtual machine directories. For more information, see Configure Virtual Machine Swapfile Properties for the Host section in the vSphere Resource Management guide.
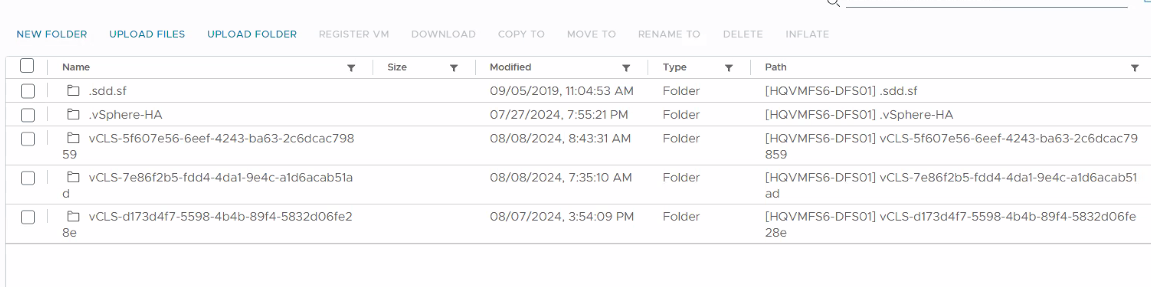
If unmounting a datastore fails because vCLS is configured to the datastore, then see External vCLS Datastore Placement to manage datastore placement for vCLS virtual machines.
If unmounting a datastore fails because the underlying filesystem is busy, then perform these steps.
- If ESXi coredump is configured to a file on the datastore, move ESXi coredump to a file on this datastore. To check and move ESXi coredump to a file on this datastore and retry the unmount operation, see Deactivate and Delete a Core Dump File .
Ensure that there is another active coredump partition or a file configured on another datastore on the host. To configure a coredump partition, see Configuring a diagnostic coredump partition on an ESXi host.
To configure coredump to a file on another datastore, see Configuring ESXi coredump to file instead of partition. - If ESXi logging is configured to use this datastore, then reconfigure syslog to use a different datastore. To check and reconfigure syslog and retry the unmount operation, see Configuring syslog on ESXi.
- If ScratchConfig.CurrentScratchLocation is configured to use the datastore, then see Creating a persistent scratch location for ESXi 8.x/7.x/6.x
.
Additional Information
Feedback
Yes
No
