VMK interfaces on ENS-p Host switch (Uplink Lag) stops working after changing Numa settings
Article ID: 345721
Updated On:
Products
VMware
VMware Telco Cloud Automation
Issue/Introduction
Symptoms:
When the lcore assignments on the NUMA nodes are changed, tunnels go down on the edge and host nodes causing the data path traffic to be broken.
To confirm that the tunnels are down on the ESXi hosts, execute the following command on all the ESXi hosts and check the status under the ‘local_state’ column:
# nsxdp-cli bfd sessions list
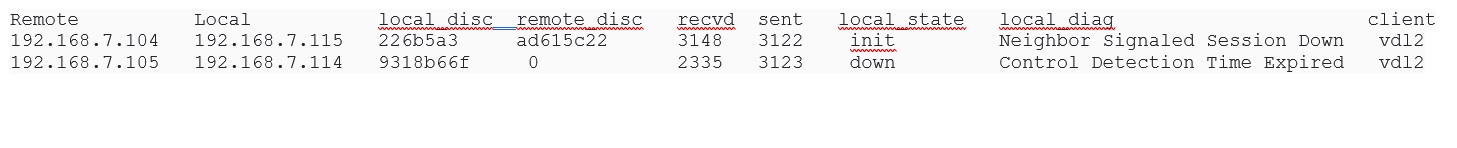
When the lcore assignments on the NUMA nodes are changed, tunnels go down on the edge and host nodes causing the data path traffic to be broken.
To confirm that the tunnels are down on the ESXi hosts, execute the following command on all the ESXi hosts and check the status under the ‘local_state’ column:
# nsxdp-cli bfd sessions list
Environment
VMware Telco Cloud Automation 1.x
Cause
- When users modify the lcore assignments on existing NUMA node
or
- When users add/remove an additional NUMA node with lcores assigned
or
- When users add/remove an additional NUMA node with lcores assigned
Resolution
This is a known issue affecting NSX-T 3.1.2
Workaround:
To apply the workaround for this issue, you must use the following procedure to disable and enable the ENS on all the transport nodes of the ENS enabled cluster.
1. To find out the ENS enabled uplinks on the ESXi hosts execute the below command to confirm which of the uplinks that are ENS capable and ENS driven(highlighted text below):
# esxcfg-nics -e
2. To get the DvsPortset-name on which the ENS enabled uplinks (of the ESXi hosts) reside, execute the below command on all the ESXi hosts:
#net-stats -l
From the above output we gather that vmnic4 and vmnic5 which are the ENS enabled uplinks on the transport node are bound to DvsPortset-1.
3. Disable ENS on all the transport nodes of the ENS enabled cluster by executing the below command on all the ESXi hosts sequentially:
#esxcfg-vswitch -Y <DvsPortset-name>
Example: #esxcfg-vswitch -Y DvsPortset-1
Note: The successful execution of the above command will not return any output but will just give back the command prompt without any errors.
4. Wait for 10 seconds and enable ENS on all the transport nodes of the ENS enabled cluster by executing the below command on all the ESXi hosts sequentially:
#esxcfg-vswitch -y <DvsPortset-name>
Example: #esxcfg-vswitch -y DvsPortset-1
Note: The successful execution of the above command will not return any output but will just give back the command prompt without any errors.
Verification
After executing the commands in steps 3 and 4 above, verify the tunnels are up on the transport nodes by executing the below command and confirm that the status of the tunnels is ‘up’ by checking the status under the ‘local_state’ column:
# nsxdp-cli bfd sessions list
Feedback
Yes
No
