Dell EMC NetWorker 18.2 for VMware Cloud on AWS
Article ID: 323639
Updated On:
Products
VMware Cloud on AWS
Issue/Introduction
This article provides information about Dell EMC NetWorker 18.2 support for VMware Cloud on AWS. With Dell EMC NetWorker 18.2, you can administrate backup, cloning and restore operations in VMware Cloud on AWS environments.
Disclaimer: The partner solution referenced in this article is a solution that is developed and supported by a partner. Use of this product is also governed by the end user license agreement of the partner. You must obtain from the partner the application, support, and licensing for using this product. For more information, see Dell EMC NetWorker.
Disclaimer: The partner solution referenced in this article is a solution that is developed and supported by a partner. Use of this product is also governed by the end user license agreement of the partner. You must obtain from the partner the application, support, and licensing for using this product. For more information, see Dell EMC NetWorker.
Resolution
Summary of target use cases, solution architecture, solution components, and support information:
Dell EMC NetWorker 18.2 and later releases provide you with the ability to perform virtual machine protection and recovery by using the Dell EMC NetWorker VMware Protection solution with the vProxy appliance, also known as NVP. Refer to the Dell EMC NetWorker 18.2 VMware integration guide for all the supported usecases for image based virtual machine protection.
Dell EMC NetWorker 18.2 and later releases also provide you with CloudBoost integration for easily storing backups in S3 cloud object storage, including short term backups for operational recovery and long term retention backups for compliance. This capability is currently available with both in-guest filesystem agents as well as a broad range of application modules for Dell EMC NetWorker. Cloning of vProxy backups to cloud object storage is supported via the CloudBoost appliance. For all the supported usecases for backup to AWS-S3, refer Dell EMC NetWorker 18.2 CloudBoost Integration Guide.
Use cases that are not supported on VMware Cloud on AWS
Some of the VMware features and permissions are not granted within the VMware Cloud on AWS (VMC) environment. Thus, some dependent Dell EMC NetWorker features will be limited or not operating. Depending on VMware update releases for VMware Cloud on AWS, the situation may change and the features listed below may become available to be qualified and supported by Dell EMC.
Dell EMC NetWorker VMware Protection in VMware Cloud on AWS does not currently support the following operations:
Dell EMC NetWorker VMware Protection solution in VMware Cloud on AWS requires the following virtual appliances:
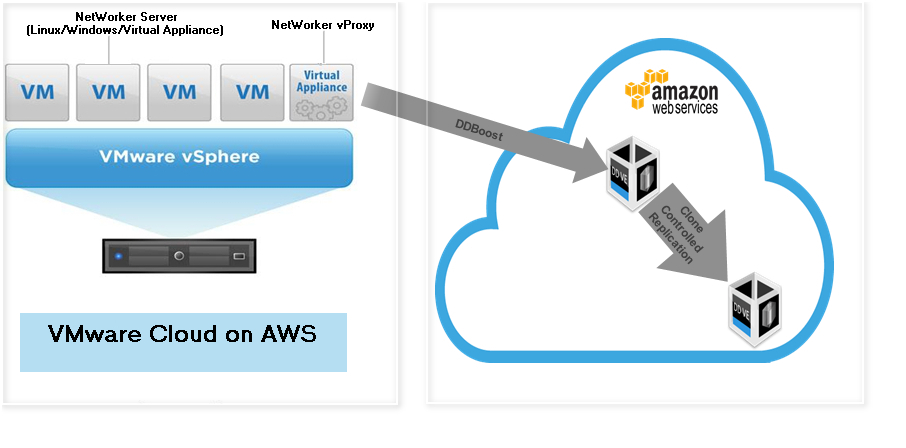
To perform data protection and disaster recovery tasks in VMware Cloud on AWS, consider the following recommendations and requirements on the backup infrastructure deployment:
The Dell EMC NetWorker 18.2 VMware integration guide provides details on how to set up and configure the NVP solution for VMware Cloud on AWS.
The Dell EMC NetWorker with CloudBoost solution is supported for a variety of filesystems as well as broad range of application modules. vProxy backups are currently not supported with CloudBoost, however cloning of vProxy backups to Amazon cloud object storage is supported via the CloudBoost appliance. The Dell EMC NetWorker CloudBoost software compatibility matrix provides more details on the supported and unsupported workflows.
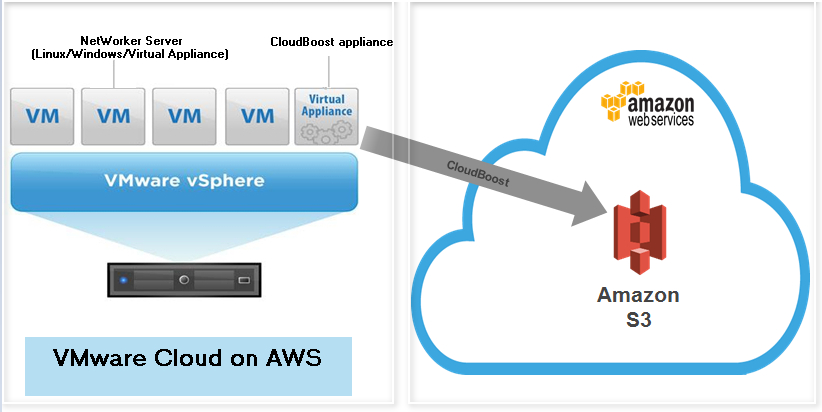
Configuring the Dell EMC NetWorker with CloudBoost solution in VMware Cloud on AWS requires the following software and virtual appliances:
VMware Cloud on AWS web portal console
In the “VMware Cloud on AWS” web portal console please ensure the following:
In the “Amazon AWS” web portal, note the following requirements:
vCenter Server inventory
In the vCenter server inventory of your SDDC, note the following requirements: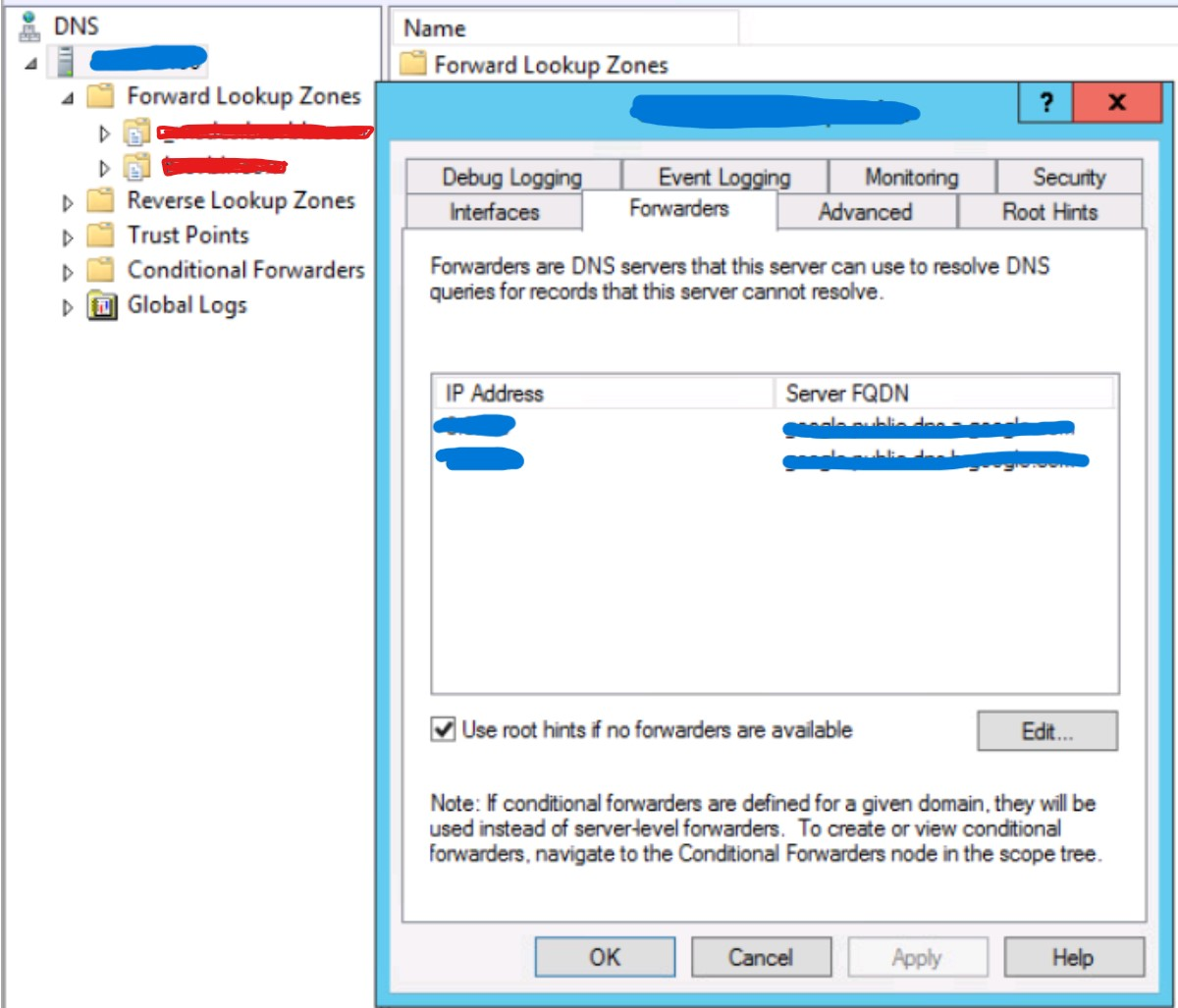
Interoperability with VMware Cloud on AWS product features
VMware Cloud on AWS has certain restrictions when it comes to workloads and resource pools. For proper operation, you can select the specific areas marked as “Workload” or “Compute”. Avoid using the non-accessible areas, for example:
Configuration best practices
Target usecases
Use cases that are supported on VMware Cloud on AWSDell EMC NetWorker 18.2 and later releases provide you with the ability to perform virtual machine protection and recovery by using the Dell EMC NetWorker VMware Protection solution with the vProxy appliance, also known as NVP. Refer to the Dell EMC NetWorker 18.2 VMware integration guide for all the supported usecases for image based virtual machine protection.
Dell EMC NetWorker 18.2 and later releases also provide you with CloudBoost integration for easily storing backups in S3 cloud object storage, including short term backups for operational recovery and long term retention backups for compliance. This capability is currently available with both in-guest filesystem agents as well as a broad range of application modules for Dell EMC NetWorker. Cloning of vProxy backups to cloud object storage is supported via the CloudBoost appliance. For all the supported usecases for backup to AWS-S3, refer Dell EMC NetWorker 18.2 CloudBoost Integration Guide.
Use cases that are not supported on VMware Cloud on AWS
Some of the VMware features and permissions are not granted within the VMware Cloud on AWS (VMC) environment. Thus, some dependent Dell EMC NetWorker features will be limited or not operating. Depending on VMware update releases for VMware Cloud on AWS, the situation may change and the features listed below may become available to be qualified and supported by Dell EMC.
Dell EMC NetWorker VMware Protection in VMware Cloud on AWS does not currently support the following operations:
- File-level restore from an image-level backup.
- Instant access recovery of an image-level backup.
- Emergency restore (image-level restore directly to an ESXi host, bypassing the vCenter).
- Image-level backups and restores using NBD or NBDSSL transport mode.
- vProxy appliance configured with “dual stack” or “IPv6 only” is not supported.
- Application-consistent data protection for MS-SQL with the vProxy appliance.
- If datacenter is placed inside a folder in the SDDC, image backup and restore is not supported
- vProxy backups are currently not supported with CloudBoost, however cloning of vProxy backups to cloud object storage is supported via the CloudBoost appliance.
- Use of the VM Backup and Recovery plugin(flash or HTML5) for vSphere
Dell EMC NetWorker VMware Protection for VMware Cloud on AWS
This solution allows image based (via VADP) data protection for the workloads running in VMware Cloud on AWS.Dell EMC NetWorker VMware Protection solution in VMware Cloud on AWS requires the following virtual appliances:
- Dell EMC NetWorker Server 18.2 or later, running on supported Windows, Linux platforms or as a NetWorker Virtual Edition (NVE)
- Data Domain Virtual Edition (DDVE) version 3.1 or later
- vProxy appliance version 3.0.0.4 or later
To perform data protection and disaster recovery tasks in VMware Cloud on AWS, consider the following recommendations and requirements on the backup infrastructure deployment:
- NetWorker Server: it is recommended to deploy Dell EMC NetWorker server in VMware Cloud on AWS environment. The machine can either run supported Linux or Windows platforms or as a virtual appliance (NVE).
- NetWorker vProxy: it is recommended to deploy the vProxy appliance in VMware Cloud on AWS environment. Deploy at least one vProxy per each SDDC cluster in the VMware Cloud on AWS.
- Data Domain Virtual Edition: it is recommended to have your backups stored outside of the VMware Cloud on AWS environment, for example, on the Amazon AWS VPC. This type of deployment allows for efficient data transfer over the fast ENI connection used by VMware to communicate with Amazon AWS.
The Dell EMC NetWorker 18.2 VMware integration guide provides details on how to set up and configure the NVP solution for VMware Cloud on AWS.
Dell EMC NetWorker CloudBoost solution for VMware Cloud on AWS
This solution allows clients to send backups directly to the object store with only the metadata being stored in the CloudBoost appliance. This distributed model where the CloudBoost appliance is not in the data path provides enhanced backup performance, scale, and client-side data reduction. The solution supports Client Direct backup to the cloud for Linux and Windows file systems and a broad range of enterprise applications. For applications that do not support Client Direct, use an external Dell EMC NetWorker Storage Node to perform backups directly to the cloud.The Dell EMC NetWorker with CloudBoost solution is supported for a variety of filesystems as well as broad range of application modules. vProxy backups are currently not supported with CloudBoost, however cloning of vProxy backups to Amazon cloud object storage is supported via the CloudBoost appliance. The Dell EMC NetWorker CloudBoost software compatibility matrix provides more details on the supported and unsupported workflows.
Configuring the Dell EMC NetWorker with CloudBoost solution in VMware Cloud on AWS requires the following software and virtual appliances:
- Dell EMC NetWorker Server 18.2 or later version, running on either supported Windows or Linux virtual machines or NetWorker Virtual Edition (NVE)
- CloudBoost appliance.
- It is recommended that an Elastic Network Interface (ENI) is already configured, allowing your SDDC and services in the AWS VPC and subnet in your AWS account to communicate without needing to route traffic through the internet gateway. This enables CloudBoost appliance to use the ENI channel to send backup data directly to the S3 cloud object storage residing in the AWS VPC, as a preferred data path for the backups to the cloud.
- It is recommended to install the CloudBoost appliance in the SDDC vCenter environment instead of installing the appliance inside the AWS VPC. Dell EMC NetWorker 18.2 CloudBoost Integration Guide provides details on how to set up and configure the CloudBoost solution.
VMware Cloud on AWS Network configuration
Domain Name System (DNS) resolution is critical for Dell EMC NetWorker deployment and configuration. All infrastructure components should be resolvable through a fully qualified domain name (FQDN). This is especially important for the Dell EMC NetWorker Server, Dell EMC NetWorker vProxy, Data Domain appliance, and CloudBoost appliance. Resolvable means that components are accessible through both forward (A) and reverse (PTR) look-ups. Review the following prerequisites prior to configuring Dell EMC NetWorker in a VMware Cloud on AWS. Also, ensure that you plan your firewall according to these prerequisites.VMware Cloud on AWS web portal console
In the “VMware Cloud on AWS” web portal console please ensure the following:
- By default, there is no external access to the vCenter Server system in your SDDC (Software Defined Data Center). You can open access to your vCenter Server system by configuring a firewall rule. Set the firewall rule in the compute gateway of VMware Cloud on AWS to enable communication to the vCenter public IP address and tcp port 443 from the desired logical network of your SDDC. The Dell EMC NetWorker server will not allow you to add the vCenter Server if this firewall rule is not configured in the SDDC.
- The default compute gateway firewall rules prevent all virtual machine traffic from reaching the internet. To allow your Dell EMC NetWorker Server virtual machine to connect to the internet, you need to create a compute gateway firewall rule to allow outbound traffic on the logical network that your Dell EMC NetWorker Server virtual machine is connected to.
- Configure DNS to allow machines in your SDDC to resolve fully-qualified domain names (FQDNs) to IP addresses belonging to the internet. The Dell EMC NetWorker Server will not allow you to add the vCenter Server using the server's public FQDN or IP address if the DNS server is not configured in your SDDC.
- It is recommended that you deploy the Data Domain system as a virtual appliance in the Amazon VPC (Virtual Private Cloud) of your choice. During the SDDC creation, ensure that you connect your SDDC to an AWS account, and select a VPC and subnet within that account.
- The Data Domain system running in your Amazon VPC must be connected to your VMware SDDC by way of the VMware Cloud Elastic Network Interfaces (ENIs), allowing your SDDC and services in the AWS VPC and subnet in your AWS account to communicate without needing to route traffic through the internet gateway.
- Detailed steps on configuring ENI are provided by VMware at https://vmc.vmware.com/console/aws-link
- Ensure that you configure the inbound and outbound firewall rules of your compute gateway for Data Domain connectivity if DDVE is running in your Amazon VPC.
- If using NSX-T then you need to configure the DNS to resolve to internal IP address of the vCenter (Go to your SDDC Management – Settings – vCenter FQDN and select the Private vCenter IP address) so that you can directly access the management network over the built-in firewall. TCP Port 443 of the vCenter needs to be opened in both the management gateway as well as compute gateway.
In the “Amazon AWS” web portal, note the following requirements:
- Configure the inbound and outbound firewall rules of your Amazon VPC security group to provide connectivity between the VMware SDDC compute gateway and Data Domain connectivity if Data Domain is running in your Amazon VPC.
- If replicating from one Data Domain system to another, ensure that you configure the inbound rule for the security group in AWS to allow all traffic from the respective private IPs of Data Domain Virtual Editions running in your Amazon VPC.
- If you have more than one Data Domain running in AWS to perform replication, then ensure that both Data Domain systems can ping each other using the FQDNs.
vCenter Server inventory
In the vCenter server inventory of your SDDC, note the following requirements:
- An internal DNS name lookup server must be running inside the vCenter inventory. This will be referenced by all the workloads running in the VMware SDDC.
- The internal DNS server must have Forwarders enabled to access the internet. This is required in order to resolve the vCenter Server's public FQDN
Interoperability with VMware Cloud on AWS product features
VMware Cloud on AWS has certain restrictions when it comes to workloads and resource pools. For proper operation, you can select the specific areas marked as “Workload” or “Compute”. Avoid using the non-accessible areas, for example:
- vsanDatastore datastore
- Management VMs folder in VMs and Templates view
- Mgmt-ResourcePool resource pool in Hosts and Clusters view
Configuration best practices
- When deploying or configuring the Dell EMC NetWorker server or vProxy, please ensure that correct DNS server IP pointing to the internal DNS server running in the vCenter inventory is specified.
- Also ensure that both forward and reverse lookup entries in the internal DNS server are in place for all the required components such as Dell EMC NetWorker server, Dell EMC NetWorker vProxy, DDVE, CloudBoost appliance etc.
- When adding the vCenter server to NMC’s VMware View, ensure you select the “Deployed in Cloud” checkbox
Note: This setting is mandatory for any vCenters running in VMware cloud on AWS, if not selected then few of the Dell EMC NetWorker operations will fail in the VMware cloud on AWS environment.
- If using NSX-T, add the vCenter server to the Dell EMC NetWorker server using either the private IP address or the FQDN, it is recommended to use FQDN.
- If using NSX-V, add the vCenter server to the Dell EMC NetWorker server using either the public FQDN of the vCenter server or the public IP address of the vCenter server. It is recommended to use FQDN.
- While adding the vCenter server to the Dell EMC NetWorker server, specify the login credentials for the cloudadmin account.
- While configuring the vProxy in the Dell EMC NetWorker server, ensure you set vProxy “Maximum NBD sessions” to zero.
VMware Cloud on AWS does not support NBD transport mode, hence we recommend to always set the “Maximum NBD sessions” for all the vProxies to zero.
Troubleshooting
- For VMware Protection using NVP, see the Troubleshooting Data Protection Policies section of Chapter 3 Protecting virtual machines in Dell EMC NetWorker 18.2 VMware integration guide.
- For CloudBoost solution, see the Troubleshoot CloudBoost device configuration issues section of Chapter 8 - Configuring NetWorker with a CloudBoost appliance in Dell EMC NetWorker 18.2 CloudBoost Integration Guide.
Log collection
- For VMware Protection using NVP, see the NMC function to collect vProxy log bundle information section of Chapter 3 - Protecting virtual machines in Dell EMC NetWorker 18.2 VMware integration guide.
- For CloudBoost solution, see Chapter 10 - Monitoring, managing, and supporting a CloudBoost appliance in Dell EMC NetWorker 18.2 CloudBoost Integration Guide
See Also
Documentation available at https://support.emc.com/products/1095_NetWorker/Documentation/, provides additional and detailed information on setup as well as configuration for all of the solution components.Feedback
Yes
No
