HPE SimpliVity Stretched Cluster Technical Overview
Article ID: 323101
Updated On:
Products
VMware vSphere ESXi
Issue/Introduction
This article provides information about HPE SimpliVity Stretched Cluster™ technology. Details of this feature in terms of functionality, configurations requirements, failure scenarios and expected behavior are described within this article.
Environment
VMware vSphere ESXi 6.0
VMware vSphere ESXi 5.5
VMware vSphere ESXi 6.5
VMware vSphere ESXi 6.7
VMware vSphere ESXi 5.5
VMware vSphere ESXi 6.5
VMware vSphere ESXi 6.7
VMware vSphere ESXi 7.0
VMware vSphere ESXi 8.0
Resolution
-
Definitions
What is vMSC?
vSphere Metro Storage Cluster (vMSC) is a configuration for stretched storage cluster architectures that maintains data availability throughout site-wide planned or unplanned outages. HPE SimpliVity Stretched Cluster™ is similar to vMSC configuration and it is Partner supported.
What is a HPE SimpliVity Stretched Cluster™?
HPE OmniStack software guarantees that in a healthy and synchronized environment the unexpected loss of one HPE OmniStack System will not lead to data unavailability. Customers have also requested the ability to describe the most likely failure scenario where an entire group of HPE OmniStack System may be lost simultaneously, and for HPE OmniStack software to ensure that customer data remains available.
The HPE Simplivity Stretched Cluster solution works in cooperation with vSphere HA and vSphere DRS to ensure that when one or more HPE OmniStack System failures occur in a physical location, guest virtual machines can be restarted in a second location. This provides for business continuity with failover time measured in seconds.
In a HPE SimpliVity Stretched Cluster, all virtual machines in the cluster gain the benefits of this additional failure tolerance.
What is Arbiter™?
The Arbiter is a Windows based software solution deployed to a third site which has fully independent failure scenarios from either of the two Stretched Cluster sites. The arbiter will store a small amount of stateful information and participates in Stretched Cluster decisions, primarily as a tiebreaker should the two stretched cluster sites become isolated from one another.
What is Data Unavailable (DU)?
The acronym DU is used for Data Unavailable, and indicates that in a particular situation the guest virtual machine data is not available, therefore the virtual machine cannot continue to run. It is used in the failure scenario matrix below
What is a HPE SimpliVity Stretched Cluster™?
HPE OmniStack software guarantees that in a healthy and synchronized environment the unexpected loss of one HPE OmniStack System will not lead to data unavailability. Customers have also requested the ability to describe the most likely failure scenario where an entire group of HPE OmniStack System may be lost simultaneously, and for HPE OmniStack software to ensure that customer data remains available.
The HPE Simplivity Stretched Cluster solution works in cooperation with vSphere HA and vSphere DRS to ensure that when one or more HPE OmniStack System failures occur in a physical location, guest virtual machines can be restarted in a second location. This provides for business continuity with failover time measured in seconds.
In a HPE SimpliVity Stretched Cluster, all virtual machines in the cluster gain the benefits of this additional failure tolerance.
What is Arbiter™?
The Arbiter is a Windows based software solution deployed to a third site which has fully independent failure scenarios from either of the two Stretched Cluster sites. The arbiter will store a small amount of stateful information and participates in Stretched Cluster decisions, primarily as a tiebreaker should the two stretched cluster sites become isolated from one another.
What is Data Unavailable (DU)?
The acronym DU is used for Data Unavailable, and indicates that in a particular situation the guest virtual machine data is not available, therefore the virtual machine cannot continue to run. It is used in the failure scenario matrix below
-
Configuration Requirements
- HPE OmniStack software version 3.5.3 Update 1 or later is required.
- vSphere 5.5 or later is required.
- HPE OmniStack System must belong to the same ESXi Cluster with vSphere HA and automatic restart for guest virtual machines enabled.
- The storage network in each physical location must use the same subnet.
- Each physical location must provide fully independent power and communications resources that are unlikely to experience a cascade or complete failure across both locations.
For Example:
- Independent backup generators at each site ensures independent power supply should both locations fall within the same power company service.
- Fully redundant networking equipment and cabling between the locations should be used to avoid any single point of failure.
- The maximum round-trip latency on the inter-site link cannot exceed 1ms.
-
Solution Overview
Customers will express likely failure scenarios by defining availability zones. Each availability zone contains one or more HPE OmniStack System that are likely to experience a failure together. Configuration of availability zones can be performed online without disruption. This configuration can be applied to existing deployments or to new deployments. The following example deployment consists of:
- 4 HPE OmniStack System in one location, Building3
- 4 HPE OmniStack System in a second location, Building7
- 1 Arbiter Software in a third location
- 64 virtual machines running in each location; 16 per host (not shown).
For Example:
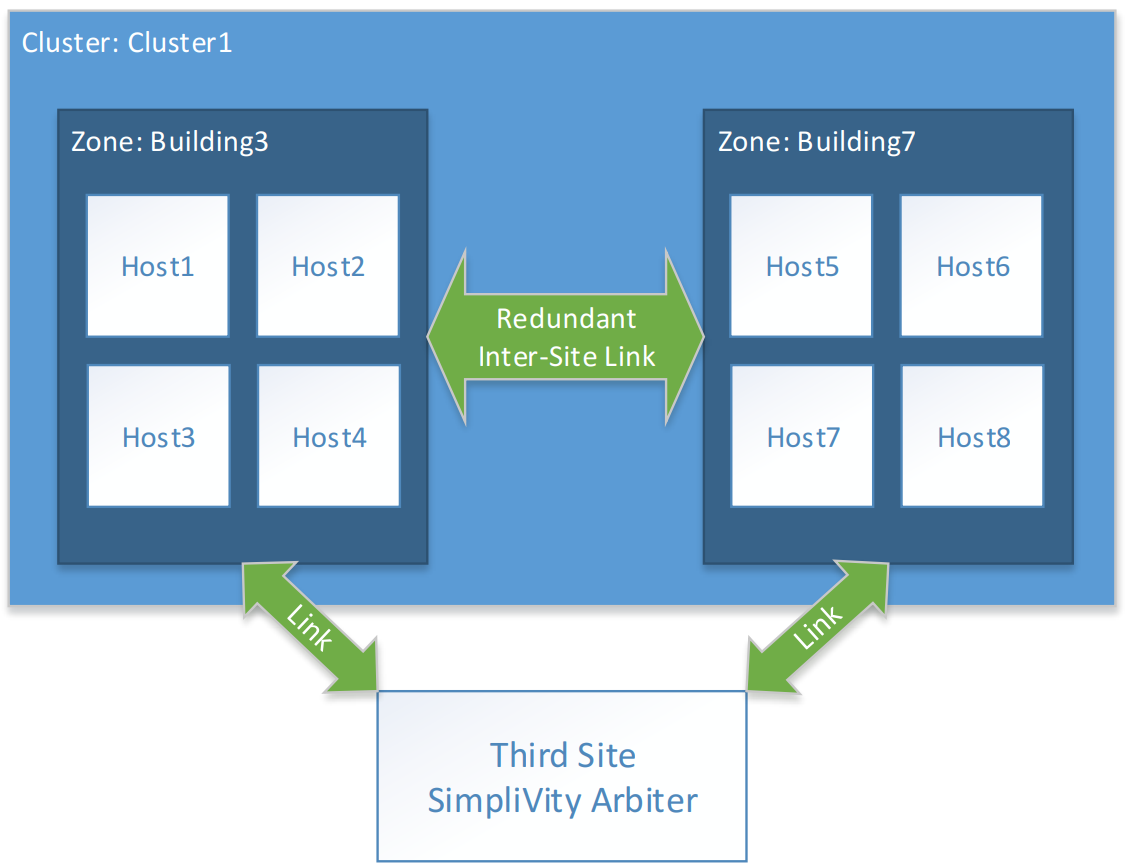
To configure this deployment, one performs availability zone configuration using the HPE SimpliVity command-line interface on any one of the hosts.
For Example:
$ SVT-ZONE-CREATE --NAME BUILDING3
$ SVT-ZONE-CREATE --NAME BUILDING7
$ SVT-ZONE-ASSIGN --ZONE BUILDING3 --HOST HOST1
$ SVT-ZONE-ASSIGN --ZONE BUILDING3 --HOST HOST2
$ SVT-ZONE-ASSIGN --ZONE BUILDING3 --HOST HOST3
$ SVT-ZONE-ASSIGN --ZONE BUILDING3 --HOST HOST4
$ SVT-ZONE-ASSIGN --ZONE BUILDING7 --HOST HOST5
$ SVT-ZONE-ASSIGN --ZONE BUILDING7 --HOST HOST6
$ SVT-ZONE-ASSIGN --ZONE BUILDING7 --HOST HOST7
$ SVT-ZONE-ASSIGN --ZONE BUILDING7 --HOST HOST8
$ SVT-ZONE-REALIZE --CLUSTER CLUSTER1
IMPACT ASSESSMENT:
14 VIRTUAL MACHINES WILL REQUIRE SOME AMOUNT OF DATA MIGRATION TO BECOME ZONE POLICY COMPLIANT. THIS WILL OCCUR AUTOMATICALLY IN THE BACKGROUND, AND MAY CAUSE A SLIGHT IMPACT TO I/O PERFORMANCE. ALL VIRTUAL MACHINES WILL REMAIN OPERATIONAL THROUGH THIS TRANSITION. EACH VIRTUAL MACHINE AFFECTED WILL RECEIVE A YELLOW ALARM INDICATING A ZONE COMPLIANCE POLICY VIOLATION WHICH WILL SELF-CLEAR WHEN THE SYSTEM REMEDIATES THE ISSUE.
DO YOU WANT TO CONTINUE [Y]?
Existing virtual machines will become zone policy compliant automatically, and all new virtual machines will be zone policy compliant implicitly. Conversion of existing virtual machines may take some time as virtual machine data may need to be reorganized align with the new cluster configuration.
vCenter Server can be migrated into the HPE SimpliVity Open Federation and run as a guest virtual machine within the HPE SimpliVity Stretched Cluster to ensure it is also highly available and will tolerate an availability zone outage within an ESXi Cluster. It will have the same failure tolerance as any other virtual machine in the stretched cluster.
To configure this deployment, one performs availability zone configuration using the HPE SimpliVity command-line interface on any one of the hosts.
For Example:
$ SVT-ZONE-CREATE --NAME BUILDING3
$ SVT-ZONE-CREATE --NAME BUILDING7
$ SVT-ZONE-ASSIGN --ZONE BUILDING3 --HOST HOST1
$ SVT-ZONE-ASSIGN --ZONE BUILDING3 --HOST HOST2
$ SVT-ZONE-ASSIGN --ZONE BUILDING3 --HOST HOST3
$ SVT-ZONE-ASSIGN --ZONE BUILDING3 --HOST HOST4
$ SVT-ZONE-ASSIGN --ZONE BUILDING7 --HOST HOST5
$ SVT-ZONE-ASSIGN --ZONE BUILDING7 --HOST HOST6
$ SVT-ZONE-ASSIGN --ZONE BUILDING7 --HOST HOST7
$ SVT-ZONE-ASSIGN --ZONE BUILDING7 --HOST HOST8
$ SVT-ZONE-REALIZE --CLUSTER CLUSTER1
IMPACT ASSESSMENT:
14 VIRTUAL MACHINES WILL REQUIRE SOME AMOUNT OF DATA MIGRATION TO BECOME ZONE POLICY COMPLIANT. THIS WILL OCCUR AUTOMATICALLY IN THE BACKGROUND, AND MAY CAUSE A SLIGHT IMPACT TO I/O PERFORMANCE. ALL VIRTUAL MACHINES WILL REMAIN OPERATIONAL THROUGH THIS TRANSITION. EACH VIRTUAL MACHINE AFFECTED WILL RECEIVE A YELLOW ALARM INDICATING A ZONE COMPLIANCE POLICY VIOLATION WHICH WILL SELF-CLEAR WHEN THE SYSTEM REMEDIATES THE ISSUE.
DO YOU WANT TO CONTINUE [Y]?
Existing virtual machines will become zone policy compliant automatically, and all new virtual machines will be zone policy compliant implicitly. Conversion of existing virtual machines may take some time as virtual machine data may need to be reorganized align with the new cluster configuration.
vCenter Server can be migrated into the HPE SimpliVity Open Federation and run as a guest virtual machine within the HPE SimpliVity Stretched Cluster to ensure it is also highly available and will tolerate an availability zone outage within an ESXi Cluster. It will have the same failure tolerance as any other virtual machine in the stretched cluster.
-
Failure Scenarios and Behavior
HPE OmniStack Virtual Controller Failure Scenarios
In these scenarios, the HPE OmniStack Virtual Controller or HPE OmniStack Accelerator experiences a failure. During these situations, the host is still running, and virtual machines on the host are still running.
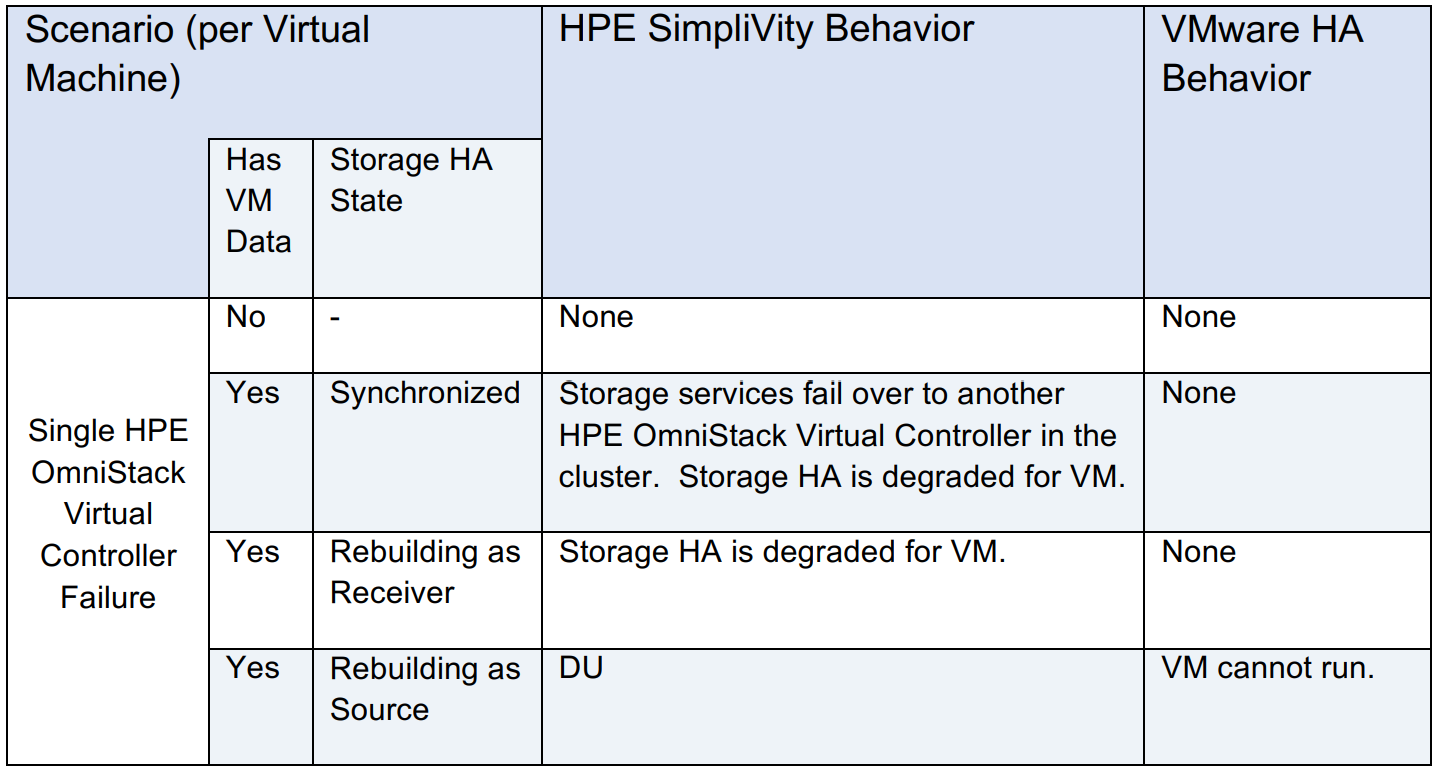
HPE OmniStack System Failures
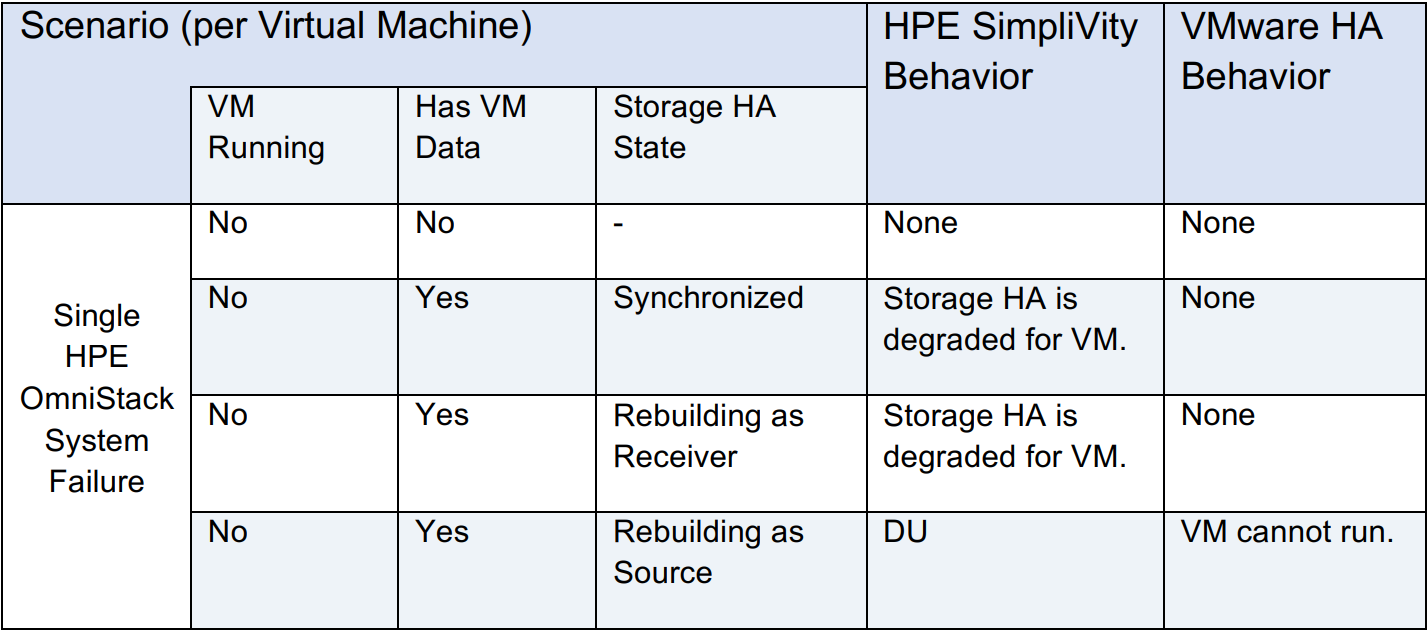
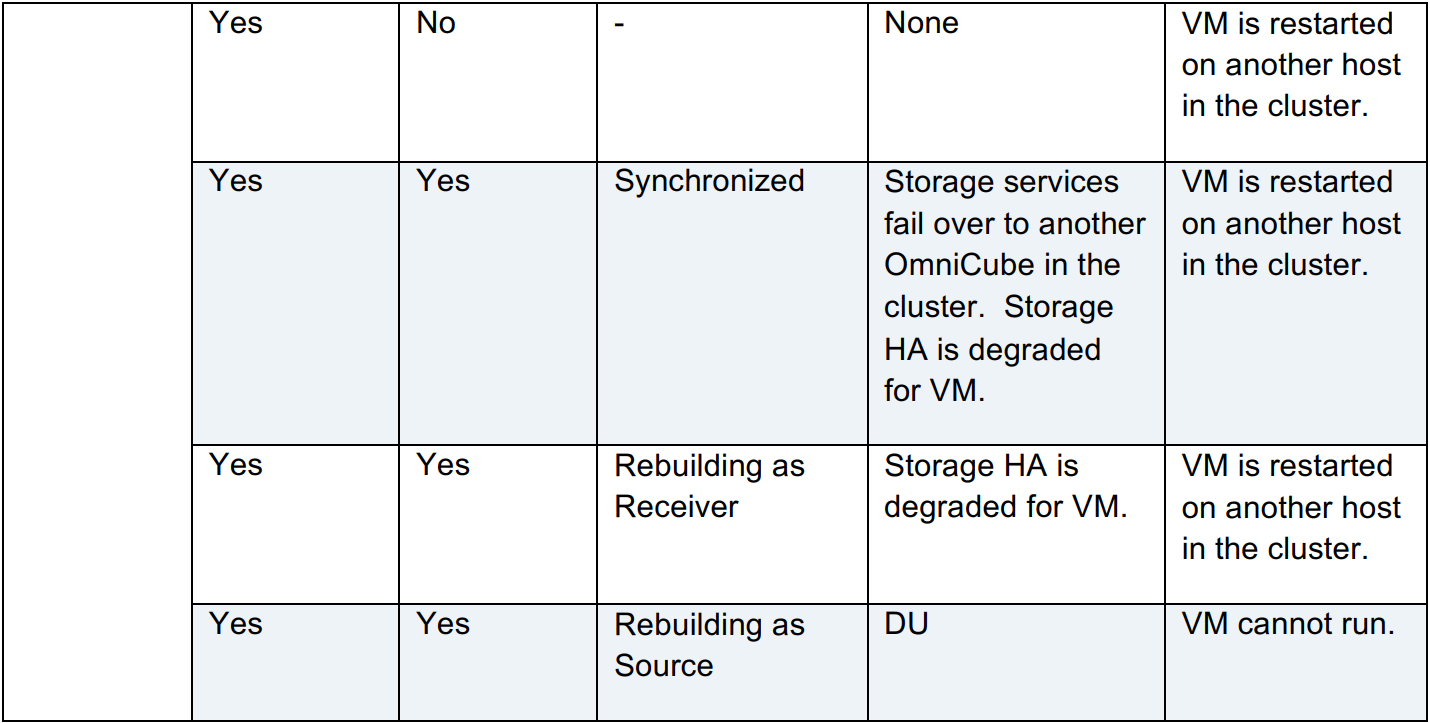
HPE OmniStack System Failures describe a situation where the hypervisor fails on an HPE SimpliVity system. These scenarios are identical to HPE OmniStack Virtual Controller Failure Scenarios, except that if a host fails where the VM was running, and there is no DU event, the VMware HA Behavior will restart the VM on another host in the cluster.
Arbiter Failure
In a situation where the arbiter becomes inaccessible with no other concurrent failures, there is no HPE SimpliVity behavior and no VMware HA behavior. An alarm is raised to vCenter Server to indicate the connectivity situation.
Availability Zone Failures
Scenarios covered up to this point are specific to a single HPE OmniStack System or HPE OmniStack Virtual Controller failure. We also need to consider the behavior when an entire availability zone is down or isolated from the rest of the cluster. In these scenarios, Site 1 and Site 2 are availability zones in a HPE SimpliVity Stretched Cluster while Site 3 is running the Arbiter.
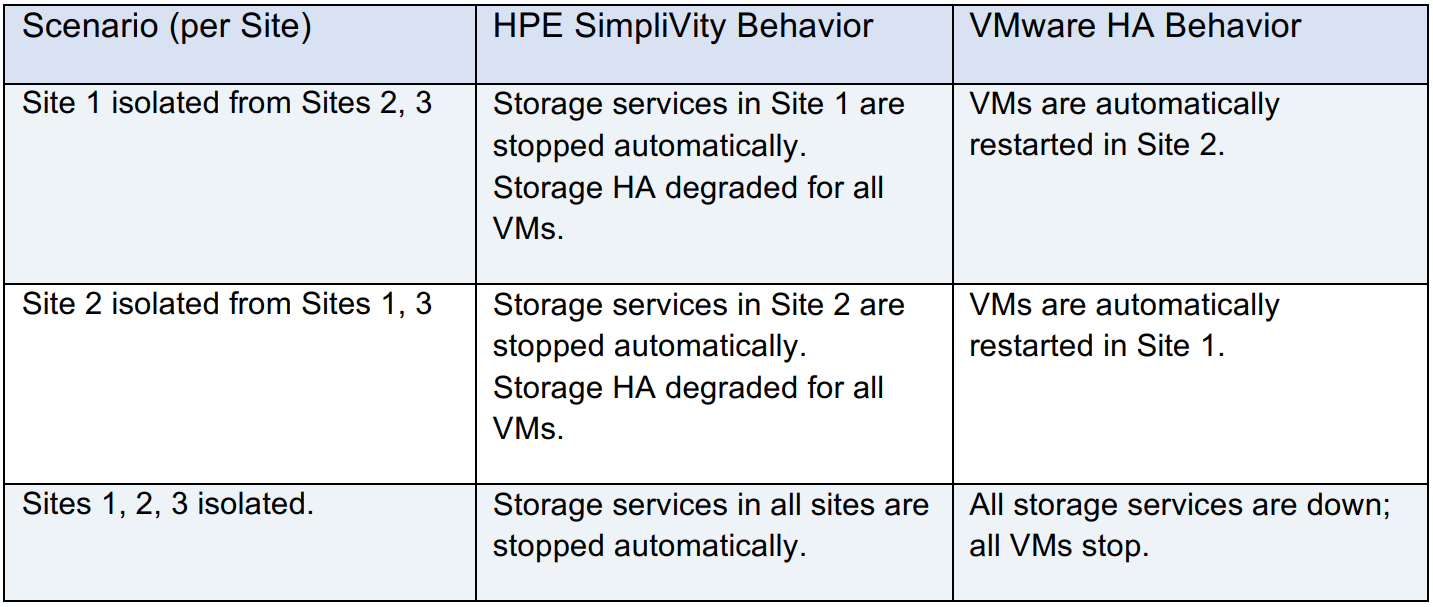
HPE OmniStack System Failures
HPE OmniStack System Failures describe a situation where the hypervisor fails on an HPE SimpliVity system. These scenarios are identical to HPE OmniStack Virtual Controller Failure Scenarios, except that if a host fails where the VM was running, and there is no DU event, the VMware HA Behavior will restart the VM on another host in the cluster.
Arbiter Failure
In a situation where the arbiter becomes inaccessible with no other concurrent failures, there is no HPE SimpliVity behavior and no VMware HA behavior. An alarm is raised to vCenter Server to indicate the connectivity situation.
Availability Zone Failures
Scenarios covered up to this point are specific to a single HPE OmniStack System or HPE OmniStack Virtual Controller failure. We also need to consider the behavior when an entire availability zone is down or isolated from the rest of the cluster. In these scenarios, Site 1 and Site 2 are availability zones in a HPE SimpliVity Stretched Cluster while Site 3 is running the Arbiter.
Additional Information
Feedback
Yes
No
