"vSAN network alarm 'RDMA Configuration Health'" warning is seen in vSAN over RDMA cluster when using async Intel icen driver
Article ID: 317243
Updated On:
Products
VMware vSAN
VMware vSphere ESXi
Issue/Introduction
This is a known cosmetic issue which does not affect vSAN over RDMA functionality.
"PFC is not Enabled" warning seen on hosts enabled for vSAN over RDMA and using Intel(R) Ethernet Network Adapter E810-XXV-2 with icen driver version 1.5.5.0 and irdman driver 1.3.3.7"
vSphere UI, vSAN cluster object: Monitor -> vSAN -> Skyline Health displays "RDMA Configuration Health" warning for each vmnic used for vSAN over RDMA.
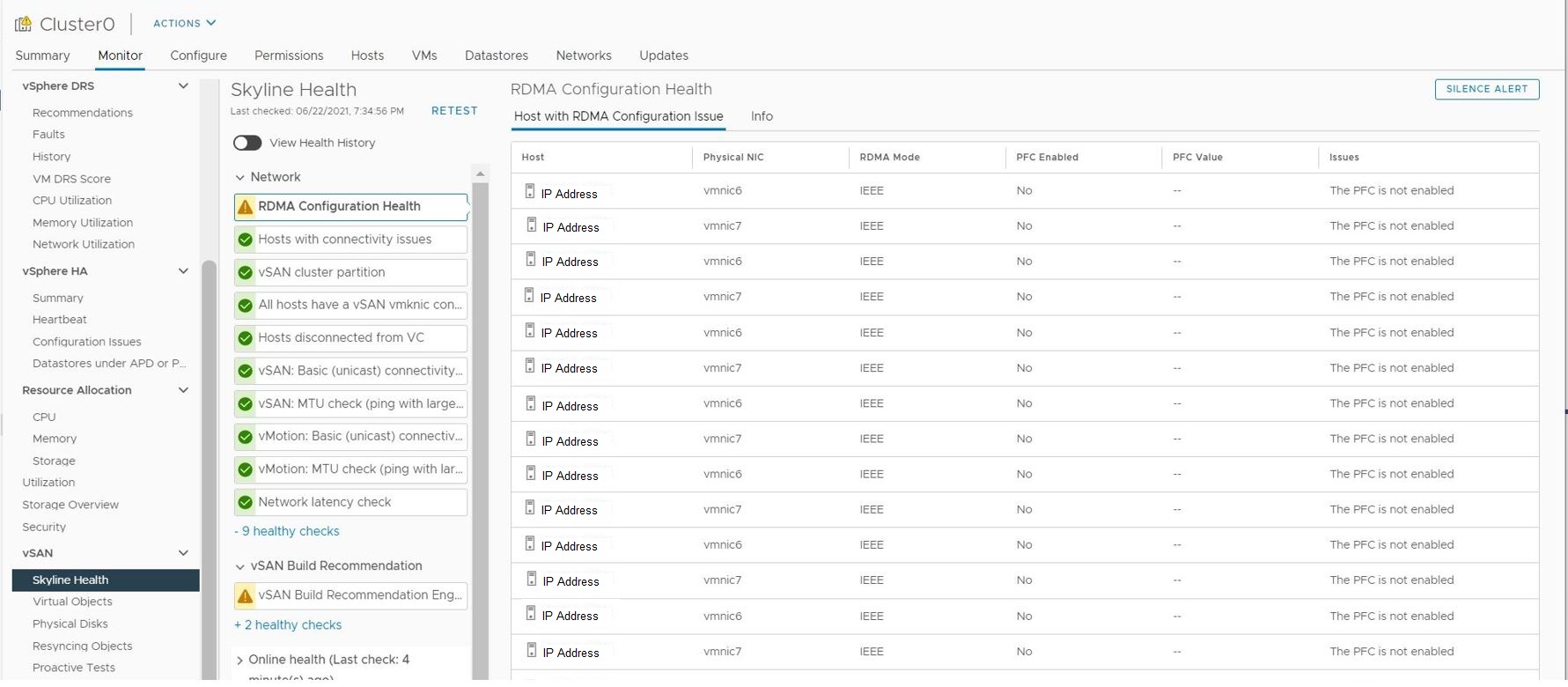
Health check displays column values for each vmnic as follows:
- RDMA Mode: IEEE
- PFC Enabled: No
- PFC value: --
- Issues: The PFC is not enabled
On an ESXi node, PFC Enabled reported as 'false' while actually enabled.
Example of configuration output for a vSAN over RDMA vmnic:
"PFC is not Enabled" warning seen on hosts enabled for vSAN over RDMA and using Intel(R) Ethernet Network Adapter E810-XXV-2 with icen driver version 1.5.5.0 and irdman driver 1.3.3.7"
vSphere UI, vSAN cluster object: Monitor -> vSAN -> Skyline Health displays "RDMA Configuration Health" warning for each vmnic used for vSAN over RDMA.
Health check displays column values for each vmnic as follows:
- RDMA Mode: IEEE
- PFC Enabled: No
- PFC value: --
- Issues: The PFC is not enabled
On an ESXi node, PFC Enabled reported as 'false' while actually enabled.
Example of configuration output for a vSAN over RDMA vmnic:
[root@esxi-host:~] esxcli network nic dcb status get -n vmnic6
Nic Name: vmnic6
Mode: 3 - IEEE Mode
Enabled: true
Capabilities:
Priority Group: true
Priority Flow Control: true
PG Traffic Classes: 8
PFC Traffic Classes: 8
PFC Enabled: false <---------------------------------- should display 'true'
PFC Configuration: 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 <------------------ should display '0 0 0 1 0 0 0 0'
IEEE ETS Configuration:
Willing Bit In ETS Config TLV: 0
Supported Capacity: 8
Credit Based Shaper ETS Algorithm Supported: 0x0
TX Bandwidth Per TC: 50 50 0 0 0 0 0 0
RX Bandwidth Per TC: 50 50 0 0 0 0 0 0
TSA Assignment Table Per TC: 2 2 0 0 0 0 0 0
Priority Assignment Per TC: 1 1 1 0 1 1 1 1
Recommended TC Bandwidth Per TC: 50 50 0 0 0 0 0 0
Recommended TSA Assignment Per TC: 2 2 0 0 0 0 0 0
Recommended Priority Assignment Per TC: 1 1 1 0 1 1 1 1
IEEE PFC Configuration:
Number Of Traffic Classes: 8
PFC Configuration: 0 0 0 1 0 0 0 0
Macsec Bypass Capability Is Enabled: 0
Round Trip Propagation Delay Of Link: 0
Sent PFC Frames: 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
Received PFC Frames: 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
DCB Apps:
App Type: L2 Ethertype
Protocol ID: 0x8906
User Priority: 0x3
App Type: L2 Ethertype
Protocol ID: 0x0
User Priority: 0x0
Nic Name: vmnic6
Mode: 3 - IEEE Mode
Enabled: true
Capabilities:
Priority Group: true
Priority Flow Control: true
PG Traffic Classes: 8
PFC Traffic Classes: 8
PFC Enabled: false <---------------------------------- should display 'true'
PFC Configuration: 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 <------------------ should display '0 0 0 1 0 0 0 0'
IEEE ETS Configuration:
Willing Bit In ETS Config TLV: 0
Supported Capacity: 8
Credit Based Shaper ETS Algorithm Supported: 0x0
TX Bandwidth Per TC: 50 50 0 0 0 0 0 0
RX Bandwidth Per TC: 50 50 0 0 0 0 0 0
TSA Assignment Table Per TC: 2 2 0 0 0 0 0 0
Priority Assignment Per TC: 1 1 1 0 1 1 1 1
Recommended TC Bandwidth Per TC: 50 50 0 0 0 0 0 0
Recommended TSA Assignment Per TC: 2 2 0 0 0 0 0 0
Recommended Priority Assignment Per TC: 1 1 1 0 1 1 1 1
IEEE PFC Configuration:
Number Of Traffic Classes: 8
PFC Configuration: 0 0 0 1 0 0 0 0
Macsec Bypass Capability Is Enabled: 0
Round Trip Propagation Delay Of Link: 0
Sent PFC Frames: 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
Received PFC Frames: 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
DCB Apps:
App Type: L2 Ethertype
Protocol ID: 0x8906
User Priority: 0x3
App Type: L2 Ethertype
Protocol ID: 0x0
User Priority: 0x0
Environment
VMware vSphere ESXi 7.0
VMware vSAN 7.0.x
VMware vSAN 7.0.x
Cause
The issue is caused by PFC enabled flag not being handled correctly in the NIC drivers and seen when NIC card is being used for vSAN over RDMA traffic. This is a driver issue, and not a vSAN issue as Skyline Health is alerting based on the misinformation gathered from the vmnic.
Affected drivers:
1. icen driver version 1.5.5.0 for Intel(R) Ethernet Network Adapter E810-XXVDA2
2. irdman driver version 1.3.3.7
The hardware vendors are working on a new NIC driver update.
Affected drivers:
1. icen driver version 1.5.5.0 for Intel(R) Ethernet Network Adapter E810-XXVDA2
2. irdman driver version 1.3.3.7
The hardware vendors are working on a new NIC driver update.
Resolution
This has been fixed in driver version 1.7.0.30
Verify the PFC with the CLI command:
$ esxcli network nic dcb status get -n vmnicX
In the output, refer to the reporting under "IEEE PFC Configuration" for "PFC Configuration: 0 0 0 1 0 0 0 0" indicates PFC enabled at priority 3.
To troubleshoot actual network connectivity issues please refer to vSAN over RDMA network design documentation and check your physical switch settings accordingly.
vSphere RDMA
Designing the vSAN Network (Using RDMA)
Affected vSphere vSAN 7.0 Update 2 and subsequent releases, using icen driver version 1.5.5.0 and irdman driver version 1.3.3.7 for vSAN over RDMA traffic.
Verify the PFC with the CLI command:
$ esxcli network nic dcb status get -n vmnicX
In the output, refer to the reporting under "IEEE PFC Configuration" for "PFC Configuration: 0 0 0 1 0 0 0 0" indicates PFC enabled at priority 3.
To troubleshoot actual network connectivity issues please refer to vSAN over RDMA network design documentation and check your physical switch settings accordingly.
vSphere RDMA
Designing the vSAN Network (Using RDMA)
Affected vSphere vSAN 7.0 Update 2 and subsequent releases, using icen driver version 1.5.5.0 and irdman driver version 1.3.3.7 for vSAN over RDMA traffic.
Additional Information
- Traditional Ethernet is a Best-Effort networking protocol. This means that under load packets are dropped and it is up to the transport protocol to cope with that loss which is dropping packets.
- DCB: The term data center bridging (DCB) refers to a collection of proposed standards designed to transform Ethernet into a lossless network with efficient Layer 2 multipath forwarding. ( standards developed by IEEE for Ethernet)
- DCB aims to eliminate loss due to queue overflow and to allocate bandwidth on links. This traffic loss is achieved via buffer queue overflow for selected traffic profiles.
- The term Lossless Ethernet is intertwined with the Data Center Bridging protocol suite (DCB) to eliminate traffic loss within an Ethernet fabric.
- Lossless Ethernet is a network that uses Data Center Bridging (DCB) to prevent packet loss.
- Lossless Ethernet networks can still drop packets in certain cases, but the amount of packet drops is significantly lower than in best-effort networks.
- A lossless network is one where the devices comprising the network fabric are configured to prevent packet loss by using DCB.
- Data Center Bridging Capability Exchange protocol (DCBX) is an extension of Link Layer Data Protocol (LLDP). If you disable LLDP on an interface, that interface cannot run DCBX.
- If you attempt to enable DCBX on an interface on which LLDP is disabled, the configuration commit operation fails.
Feedback
Yes
No
