Basic Linux commands for VCE system health check
Article ID: 301462
Updated On:
Products
VMware SD-WAN by VeloCloud
Issue/Introduction
This KB article will list frequent used Linux commands for SDWAN Edge health checking.
Environment
VMware SD-WAN by VeloCloud
Resolution
1. To verify interface state and IP address configured.
2. To monitoring interface throughput
4. To show ARP table
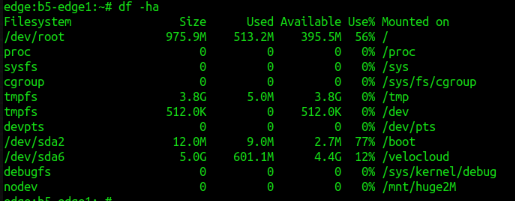
7. To report file system disk space usage
-h human-readable
-k 1024-byte blocks (default)
-m 1M-byte blocks
Sample:

or
10. To verify system time and ntp
11. To verify if DNS working
Current DNS server configured for edge self.
In case you need to restart DNS service.
12. To check http/https connectivity to destination URL (For example, you need to verify the https connection to VCO)
--interface <name> Use network INTERFACE (or address)
Please check more option detail from below URL.
https://curl.se/docs/manpage.html
Sample :
13. ping to verify network reachability.
Note : ping on edge follows 'debug.py --routes' routing table to forward packet.
Stop after sending count ECHO_REQUEST packets.
-D
Print timestamp (unix time + microseconds as in gettimeofday) before each line.
-i interval
Wait interval seconds between sending each packet.
-I interface
interface is either an address, an interface name or a VRF name. If interface is an address, it sets source address to specified interface address.
-M pmtudisc_opt ( do / dont)
Select Path MTU Discovery strategy. pmtudisc_option may be either do (prohibit fragmentation, even local one), want (do PMTU discovery, fragment locally when packet size is large), or dont (do not set DF flag).
do -- has DF flag set
dont -- has no DF flag set
-n
Numeric output only. No attempt will be made to lookup symbolic names for host addresses.
-s packetsize
Specifies the number of data bytes to be sent.
-t ttl
Set the IP Time to Live.
Sample :
or for IPv6
-s SIZE Send SIZE data bytes in packets (default 56)
-i SECS Interval
-A Ping as soon as reply is recevied
-I IFACE/IP Source interface or IP address
-q Quiet, only display output at start and when finished
-p HEXBYTE Pattern to use for payload
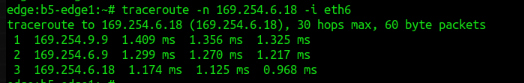
14. traceroute - print the route packets trace to network host
Note : traceroute follows Linux routing table ('route -n') to forward packets.
-i interface, --interface=interface
Specifies the interface through which traceroute should send packets. By default, the interface is selected according to the routing table.
-n Do not try to map IP addresses to host names when displaying them.
-s source_addr, --source=source_addr
Chooses an alternative source address. Note that you must select the address of one of the interfaces. By default, the address of the outgoing interface is used.
-m max_ttl, --max-hops=max_ttl
Specifies the maximum number of hops (max time-to-live value) traceroute will probe. The default is 30.
Sample :
ip address
Sample:or
ifconfig
Sample:
2. To monitoring interface throughput
ifstat [option] [delay] [count]
-i Specifies the list of interfaces to monitor, separated by commas. -b Reports bandwith in kbits/sec instead of kbytes/sec. -t Adds a timestamp at the beginning of each line. delay is the delay between updates in seconds, which defaults to 1. count is the number of updates before stopping. If not specified, it is unlimited. Sample:3. To show Linux routing table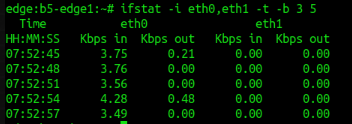
route
-n show numerical addresses instead of trying to determine symbolic host names. -A use the specified address family. (inet/inet6) Sample: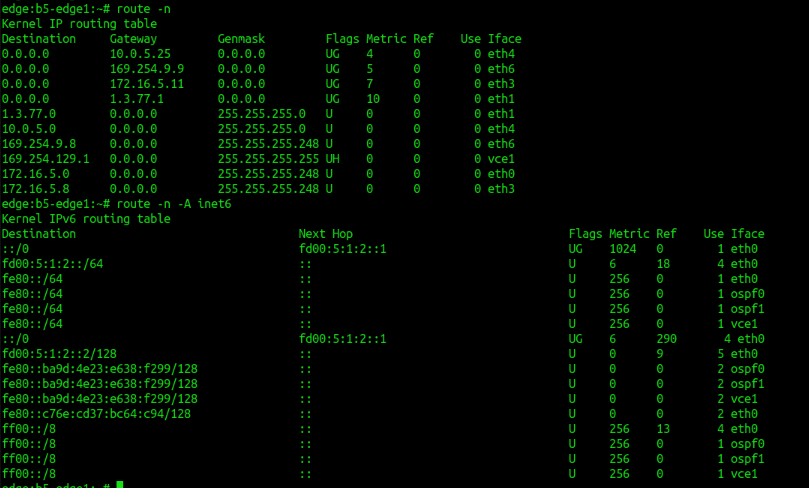
4. To show ARP table
arp -an
-a display (all) hosts in alternative (BSD) style -n, --numeric don't resolve names Sample:5. To show memory usage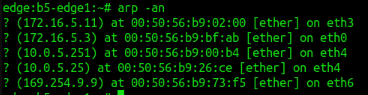
free -m
-k Display the amount of memory in kibibytes. This is the default. -m Display the amount of memory in mebibytes. -g Display the amount of memory in gibibytes. Sample:6. To show CPU utilization, load average, running processes.Output Explanation : total Total installed memory (MemTotal and SwapTotal in /proc/meminfo) used Used memory (calculated as total - free - buffers - cache) free Unused memory (MemFree and SwapFree in /proc/meminfo) shared Memory used (mostly) by tmpfs (Shmem in /proc/meminfo) buffers Memory used by kernel buffers (Buffers in /proc/meminfo) cache Memory used by the page cache and slabs (Cached and SReclaimable in /proc/meminfo) buff/cache Sum of buffers and cache available Estimation of how much memory is available for starting new applications, without swapping. Unlike the data provided by the cache or free fields, this field takes into account page cache and also that not all reclaimable memory slabs will be reclaimed due to items being in use (MemAvailable in /proc/meminfo, available on kernels 3.14, emulated on kernels 2.6.27+, otherwise the same as free)
top
-H :Threads-mode operation Instructs top to display individual threads. -n :Number-of-iterations limit as: -n number Specifies the maximum number of iterations, or frames, top should produce before ending. Sample: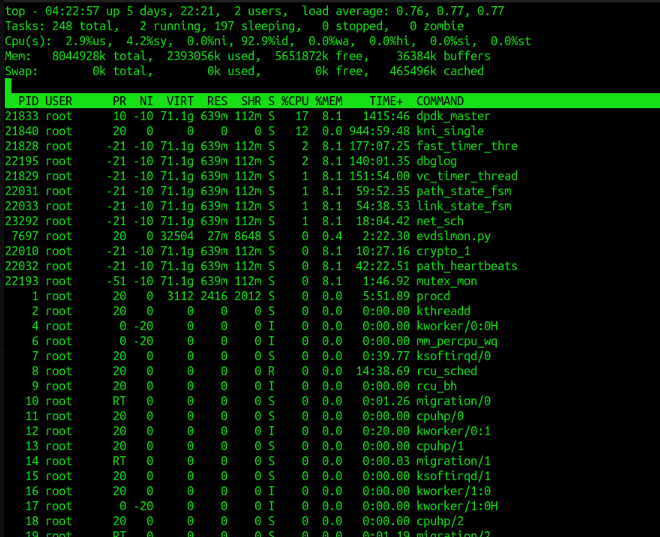
7. To report file system disk space usage
df [OPTION]-a include pseudo, duplicate, inaccessible file systems
-h human-readable
-k 1024-byte blocks (default)
-m 1M-byte blocks
Sample:
8. To show current running process
ps -ef
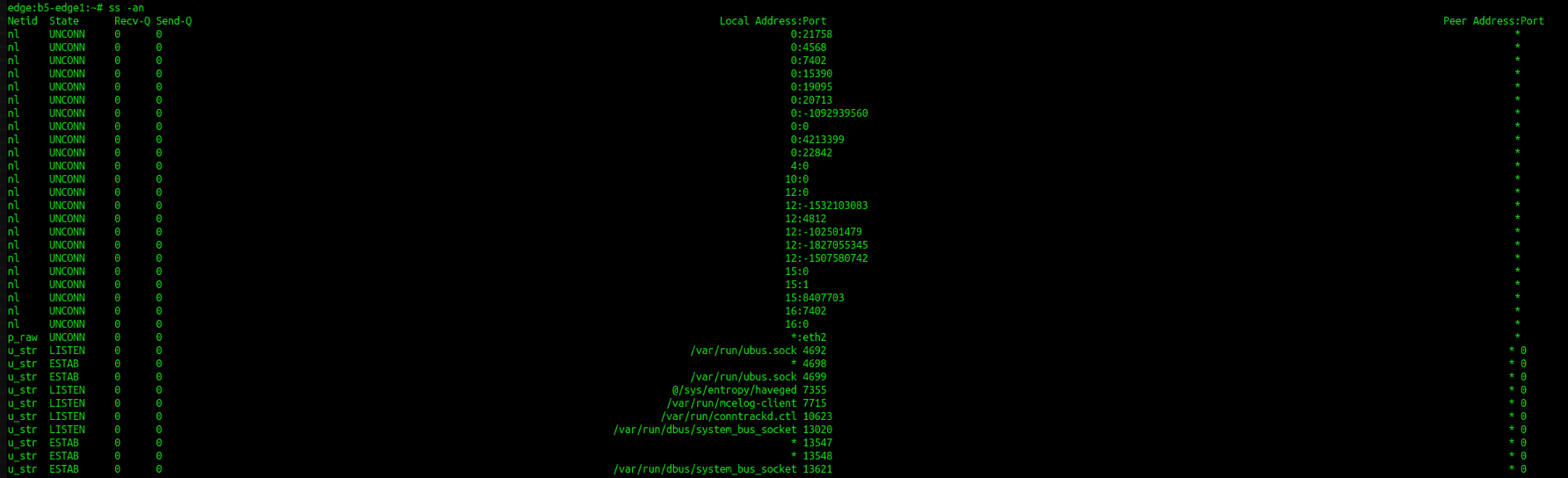
9. Show network connections and sockets
ss -an
-a display all sockets -n don't resolve service names -p show process using socketSample :
or
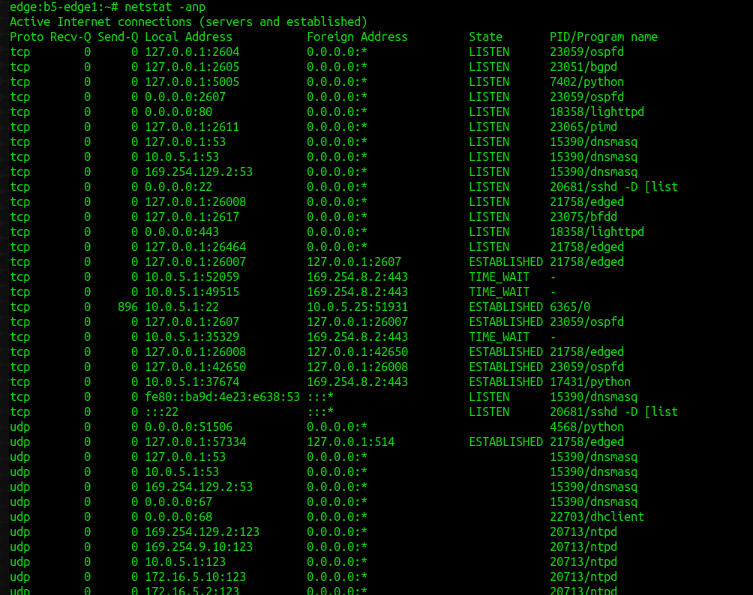
netstat -an
-a Show both listening and non-listening sockets. -p Show the PID and name of the program to which each socket belongs. -n Show numerical addresses instead of trying to determine symbolic host, port or user names.Sample :
10. To verify system time and ntp
date
and
ntpq -p
Sample :In case you need to restart ntp
/etc/init.d/ntpd restart
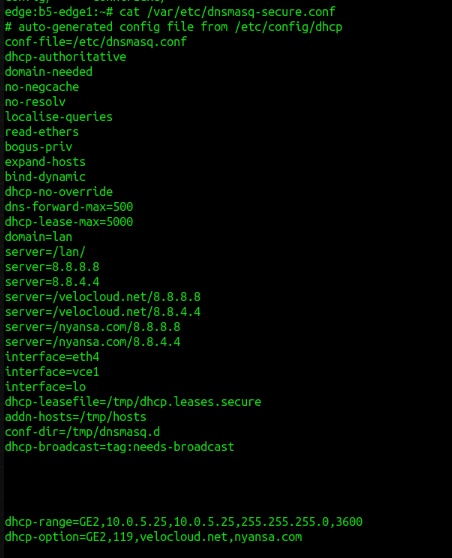
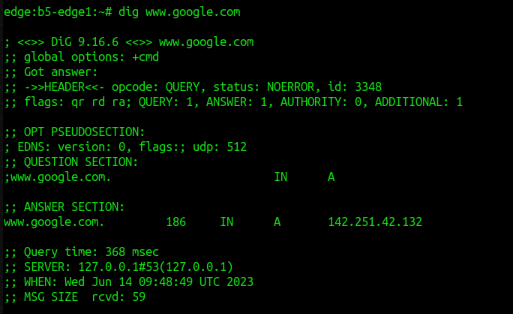
11. To verify if DNS working
Current DNS server configured for edge self.
cat /var/etc/dnsmasq-secure.confSample:
nslookup
or
dig
Sample :or use dig for DNS testingyou can change another DNS server to resolve required name.
In case you need to restart DNS service.
/etc/init.d/dnsmasq restart
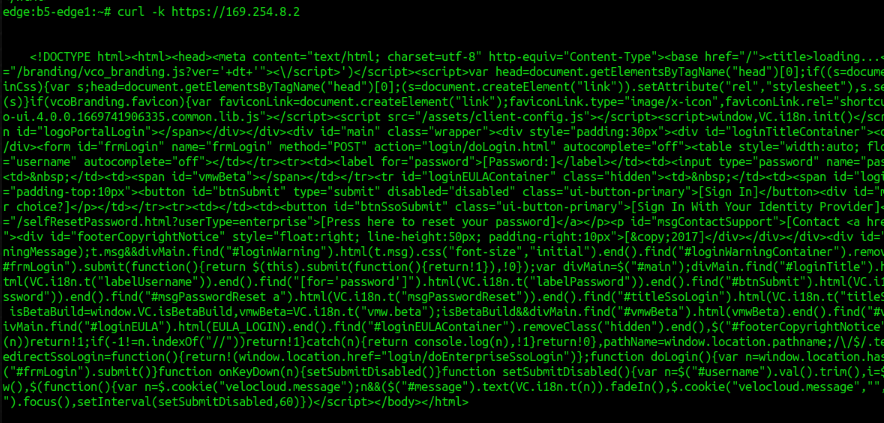
12. To check http/https connectivity to destination URL (For example, you need to verify the https connection to VCO)
curl [options / URLs]-k, --insecure Allow insecure server connections when using SSL
--interface <name> Use network INTERFACE (or address)
Please check more option detail from below URL.
https://curl.se/docs/manpage.html
Sample :
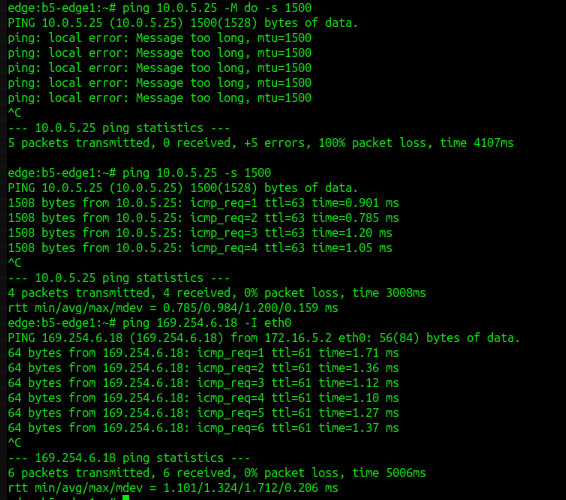
13. ping to verify network reachability.
Note : ping on edge follows 'debug.py --routes' routing table to forward packet.
ping [option] {destination}
-c countStop after sending count ECHO_REQUEST packets.
-D
Print timestamp (unix time + microseconds as in gettimeofday) before each line.
-i interval
Wait interval seconds between sending each packet.
-I interface
interface is either an address, an interface name or a VRF name. If interface is an address, it sets source address to specified interface address.
-M pmtudisc_opt ( do / dont)
Select Path MTU Discovery strategy. pmtudisc_option may be either do (prohibit fragmentation, even local one), want (do PMTU discovery, fragment locally when packet size is large), or dont (do not set DF flag).
do -- has DF flag set
dont -- has no DF flag set
-n
Numeric output only. No attempt will be made to lookup symbolic names for host addresses.
-s packetsize
Specifies the number of data bytes to be sent.
-t ttl
Set the IP Time to Live.
Sample :
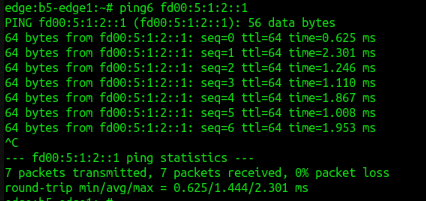
or for IPv6
ping6 [OPTIONS] {destination}
-c CNT Send only CNT pings-s SIZE Send SIZE data bytes in packets (default 56)
-i SECS Interval
-A Ping as soon as reply is recevied
-I IFACE/IP Source interface or IP address
-q Quiet, only display output at start and when finished
-p HEXBYTE Pattern to use for payload
14. traceroute - print the route packets trace to network host
Note : traceroute follows Linux routing table ('route -n') to forward packets.
traceroute [options] hostor for IPV6
traceroute6 [options] host
-i interface, --interface=interface
Specifies the interface through which traceroute should send packets. By default, the interface is selected according to the routing table.
-n Do not try to map IP addresses to host names when displaying them.
-s source_addr, --source=source_addr
Chooses an alternative source address. Note that you must select the address of one of the interfaces. By default, the address of the outgoing interface is used.
-m max_ttl, --max-hops=max_ttl
Specifies the maximum number of hops (max time-to-live value) traceroute will probe. The default is 30.
Sample :
Feedback
Yes
No
