PF reason codes in NSX-T Data Center
Article ID: 301324
Updated On:
Products
VMware NSX Firewall
VMware NSX
Issue/Introduction
This article provides information listing PF reason codes in NSX-T Data Center
Environment
VMware NSX-T Data Center 3.x
VMware NSX-T Data Center 4.x
Resolution
Distributed Firewall (DFW) tracks both the state transition of the TCP flow in both directions based upon TCP flags (SYN/ACK/FIN/RST) and the sliding sequence number window (low and high) based upon current sequence number, ack number from the peer, and the window size including the window scaling value.
DFW also does the sanity check on IP/TCP/UDP headers to ensure that the headers are valid.
DFW also deals with fragmented packets and ensures that all the fragments for a packet id are received and can be reconstructed. There is also a maximum number of pending fragment buffers to protect against a fragment attack.
DFW maintains stats for the following Drop Packet Reason Codes. The explanation of these codes and the various reasons are given here
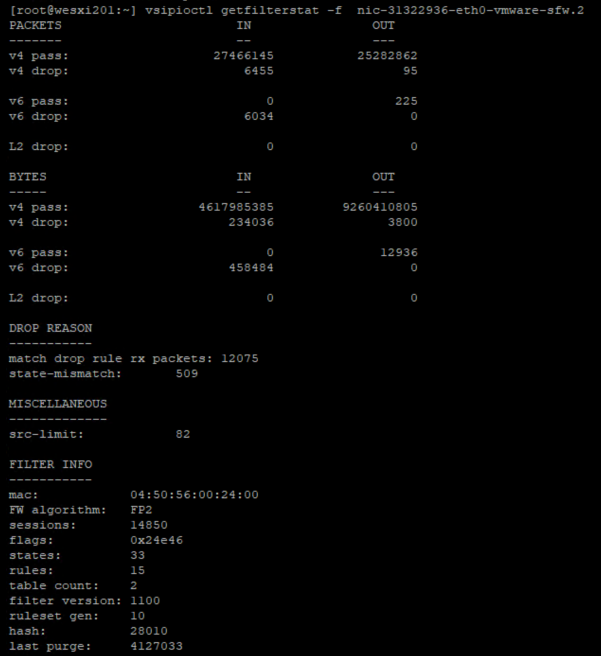
New basic output format is shown here.
Note: pass and drop counts are always displayed. The other counters are displayed if they contain non-zero values.
For example:
/root:12 > vsipioctl getfilterstat -f nic-1023172-eth0-vmware-sfw.2
DFW also does the sanity check on IP/TCP/UDP headers to ensure that the headers are valid.
DFW also deals with fragmented packets and ensures that all the fragments for a packet id are received and can be reconstructed. There is also a maximum number of pending fragment buffers to protect against a fragment attack.
DFW maintains stats for the following Drop Packet Reason Codes. The explanation of these codes and the various reasons are given here
New basic output format is shown here.
Note: pass and drop counts are always displayed. The other counters are displayed if they contain non-zero values.
For example:
/root:12 > vsipioctl getfilterstat -f nic-1023172-eth0-vmware-sfw.2
| Field | Meaning |
|---|---|
| mac | The MAC address of the vNIC (virtual NIC) to which this DFW filter is attached. |
| FW algorithm | The internal filter-pipeline version in use (e.g. “FP2” = Filter Path v2 engine). |
| sessions | Number of application-helper (ALG) or connection-tracking sessions currently held in the session table. |
| flags | A hex bitmask of enabled filter features or modes (e.g. strict TCP state, normalization, fragment handling, etc.). |
| states | Count of active state-tracking entries (bidirectional TCP/UDP flow states) in the state table. |
| rules | How many firewall rules have been loaded into this filter instance from your DFW policy. |
| table count | Number of lookup tables or pipeline stages the engine uses (for example, one for L2, one for L3/L4). |
| filter version | Internal build/release number of the dvfilter binary module that’s running on this host. |
| ruleset gen | Generation number of the currently loaded ruleset configuration—this increments every time you push a new policy. |
| hash | Integrity checksum or hash of the loaded filter code and/or ruleset, used to detect mismatches or reloads. |
| last purge | Timestamp (in seconds since the filter or host boot) when the last cleanup cycle ran to remove expired state/fragment entries. |
- Match: If a packet hits a Drop or a Reject Rule.
- State-mismatch: Caused due to detection of invalid state (TCP Flags) or TCP sequence or ack number in the packet.
Typical causes are:
- The current payloads next sequence number (current sequence number + length of tcp payload) may exceed the acceptable maximum window sequence number.
- The current payloads starting sequence number may be less than the acceptable minimum window sequence number.
- The current payloads ack number may be less or greater than the acceptable minimum window acknowledgement number.
- If TCP Strict flag is enabled, of the first packet is not a SYN packet.
- If processing an ALG packet, FTP/TFTP/ORACLE/MS-RPC/DCE-RPC, an error is encountered.
- Memory: Caused by failure to allocate memory for one of many data structures/buffers.
Typical causes are:
- Maximum number of supported states in the Host exceeded.
- Maximum number of fragment buffers per filter exceed.
- Under memory stress conditions, one of many allocation failure during packet processing.
- State Insertion: Caused by failure to insert the state in the Flow Table.
The following can happen principally because of:
- Memory constraints.
- Duplicate Session (Rarely).
- Fragment: Due to fragment handling.
Caused by:
- Invalid Fragment offset.
- Fragment reassembly timer expiring.
- ICMP error messages don't refer to non-first fragments in the inner packet.
- Short Packet: IP or Transport header length being short of minimum.
- Spoofguard: Caused by Spoofguard implementation.
Caused by:
- Invalid ARP packet mac value.
- Invalid ARP packet ip value.
- Invalid mac address.
- Invalid IP Address.
- Normalization: Invalid IP or Transport header.
Caused by:
- Invalid IP Version.
- Invalid Packet length.
- Invalid Header Length.
- IP Options: If a packet matches a rule which does not allow IP Options.
Feedback
Yes
No
