How to change the default 256 character path length limitation (MAX_PATH) in Windows
Article ID: 259160
Updated On:
Products
Issue/Introduction
Environment
Release: Windows 10, 11
Cause
By default, Windows uses a path length limitation (MAX_PATH) of 256 characters: Naming Files, Paths, and Namespaces.
Resolution
Starting in Windows 10 (Version 1607), the MAX_PATH limitations have been removed from the Common Win32 file and directory functions. To use the new extended path behavior, you must opt-in by using a registry key change.
Warning!
Problems caused by improperly editing the Windows registry could render your computer operating system unusable. Microsoft provides a wealth of critical information that you need to know about the registry in the Microsoft Knowledge Base. Use the Microsoft Registry Editor only at your own risk and only after backing up the registry as outlined for your operating system in the Microsoft article How to back up and restore the registry in Windows and in the related solution How to back up the system registry. Additional information about the registry is also contained in the Help topics in the Microsoft Registry Editor.
To enable the long path behavior in Windows 10:
- Go to Windows Start and type REGEDIT.
- Choose the Registry Editor.
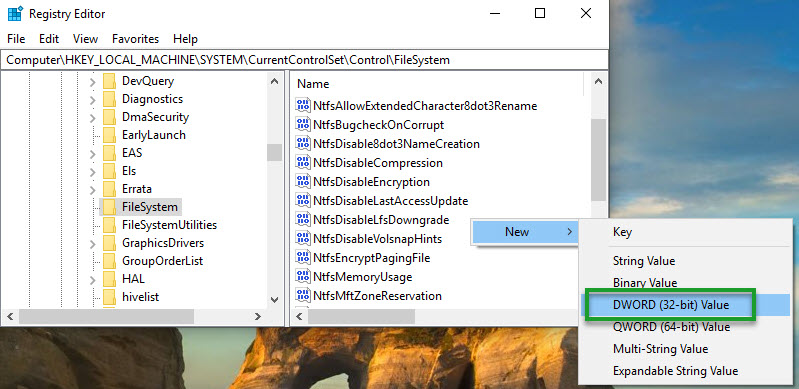
- In the Registry Editor, navigate to the following location: at HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SYSTEM\CurrentControlSet\Control\FileSystem.
- Select the entry named: LongPathsEnabled.
- With the FileSystem folder selected, right-click in the empty space of the Name column where the registry keys are located.
- Select New.
- Choose the DWORD (32-bit) Value.
- Right-click the newly added key and choose Rename.
- Name the key LongPathsEnabled.
- Press Enter.
- Double-click on the LongPathsEnabled entry to open the key.
- In the Value data field, enter a value of 1. This will enable the long paths option.
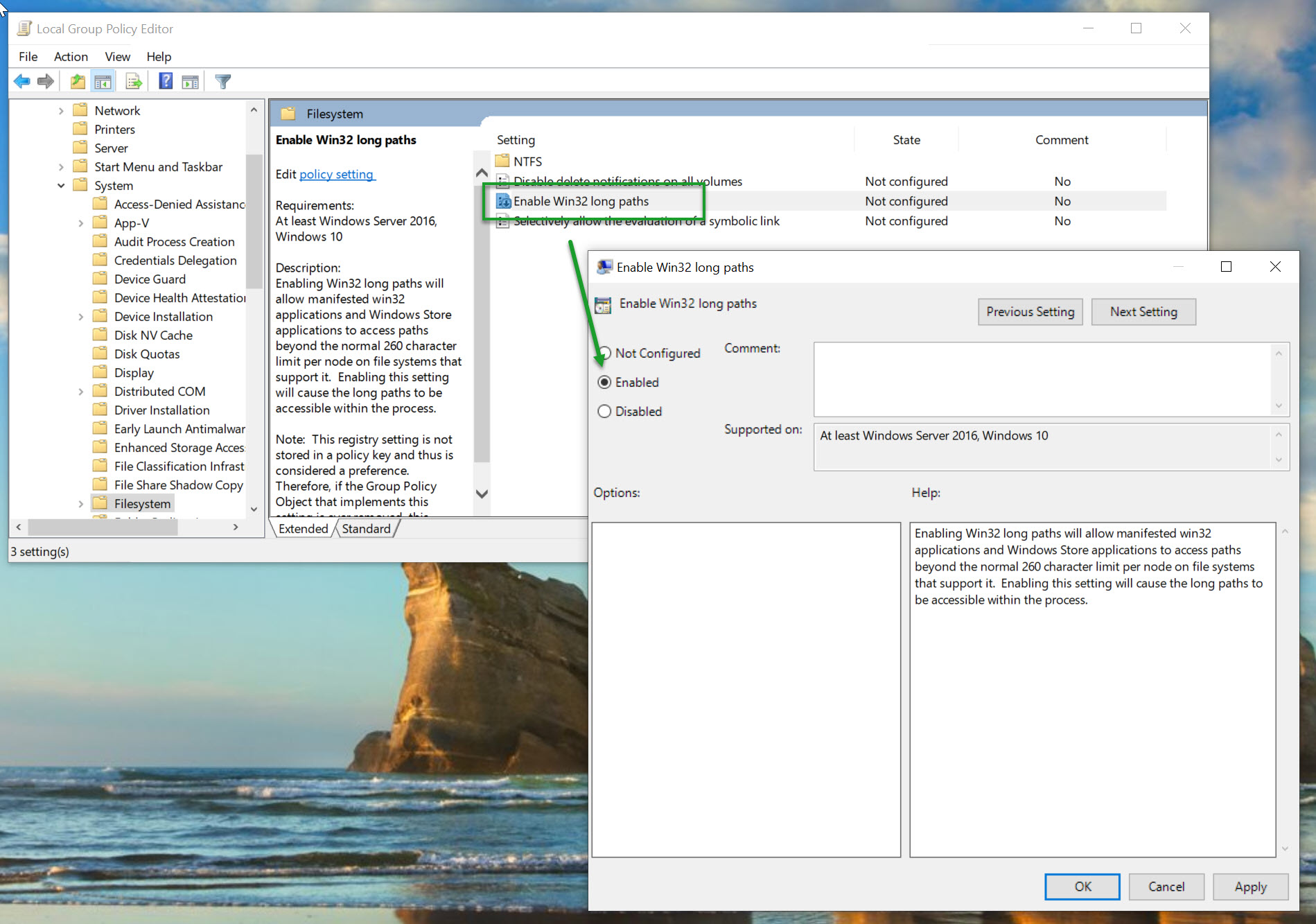
Additionally, the registry key can also be controlled via the Group Policy in Computer Configuration > Administrative Templates > System > Filesystem > Enable NTFS long paths.